This article explains SQL OUTER JOIN syntax and gives an example on how to use OUTER JOIN
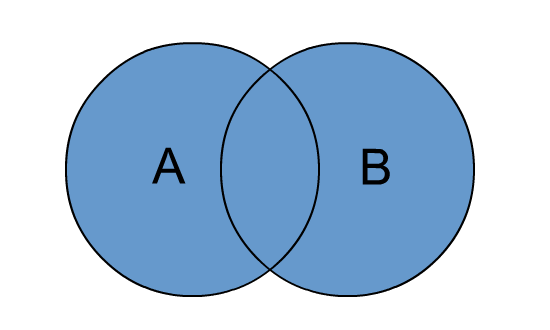
Outer join joined table will contain all records from both the tables (A and B) and fill in NULL for missing matches on either side.
OUTER JOIN and FULL JOIN are the same in terms of terminology.
You can use following links to view the different types of SQL JOINs :
Outer Join Visual Representation
Outer Join Syntax
This query will return the joined result of all records in both tables
SELECT Table_A.column1, Table_B.column2... FROM Table_A A FULL JOIN Table_B B ON A.Key = B.Key
Outer Join Example
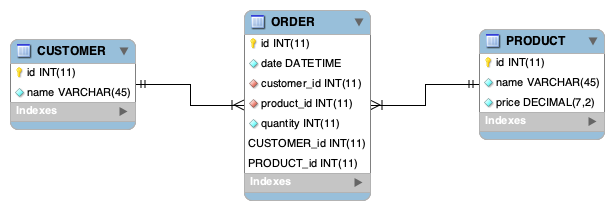
We will create 3 tables
- CUSTOMER
- PRODUCT
- ORDER
A customer can order products. In the ORDER table we hold the customer ID and the quantity of each product the customer has ordered.
Use following SQL scripts to create the three tables.
Create CUSTOMER table
CREATE TABLE `CUSTOMER` ( `id` INT NOT NULL, `name` VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`));
Create PRODUCT table
CREATE TABLE `PRODUCT` ( `id` INT NOT NULL, `name` VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL, `price` DECIMAL(7,2) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`));
Create ORDER table
CREATE TABLE `ORDER` (
`id` INT NOT NULL,
`date` DATETIME NOT NULL,
`customer_id` INT NOT NULL,
`product_id` INT NOT NULL,
`quantity` INT NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
INDEX `product_id_idx` (`product_id` ASC) VISIBLE,
INDEX `customer_id_idx` (`customer_id` ASC) VISIBLE,
CONSTRAINT `customer_id`
FOREIGN KEY (`customer_id`)
REFERENCES `CUSTOMER` (`id`),
CONSTRAINT `product_id`
FOREIGN KEY (`product_id`)
REFERENCES `PRODUCT` (`id`));
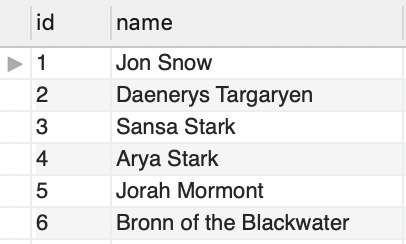
Insert data in CUSTOMER table
INSERT INTO `CUSTOMER` (`id`, `name`) VALUES ('1', 'Jon Snow');
INSERT INTO `CUSTOMER` (`id`, `name`) VALUES ('2', 'Daenerys Targaryen');
INSERT INTO `CUSTOMER` (`id`, `name`) VALUES ('3', 'Sansa Stark');
INSERT INTO `CUSTOMER` (`id`, `name`) VALUES ('4', 'Arya Stark');
INSERT INTO `CUSTOMER` (`id`, `name`) VALUES ('5', 'Jorah Mormont');
INSERT INTO `CUSTOMER` (`id`, `name`) VALUES ('6', 'Bronn of the Blackwater');
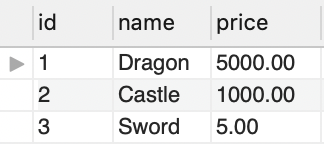
Insert data in PRODUCT table
INSERT INTO `PRODUCT` (`id`, `name`, `price`) VALUES ('1', 'Dragon', '5000');
INSERT INTO `PRODUCT` (`id`, `name`, `price`) VALUES ('2', 'Castle', '1000');
INSERT INTO `PRODUCT` (`id`, `name`, `price`) VALUES ('3', 'Sword', '5');
Insert data in ORDER table
INSERT INTO `ORDER` (`id`, `date`, `customer_id`, `product_id`, `quantity`) VALUES ('1', '2019-01-08 00:00:00', '2', '1', '3');
INSERT INTO `ORDER` (`id`, `date`, `customer_id`, `product_id`, `quantity`) VALUES ('2', '2019-01-22 00:00:00', '6', '3', '1');
INSERT INTO `ORDER` (`id`, `date`, `customer_id`, `product_id`, `quantity`) VALUES ('3', '2019-02-15 00:00:00', '6', '2', '1');
INSERT INTO `ORDER` (`id`, `date`, `customer_id`, `product_id`, `quantity`) VALUES ('4', '2019-02-16 00:00:00', '1', '3', '1');
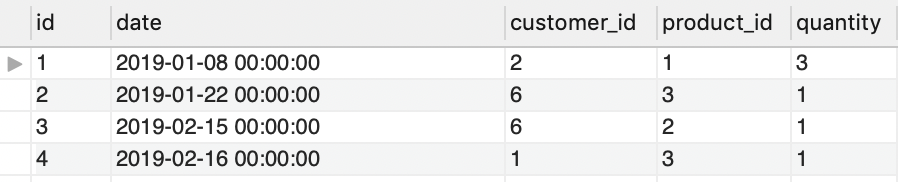
Database tables
And now that’s what we have in our tables:
Outer join tables
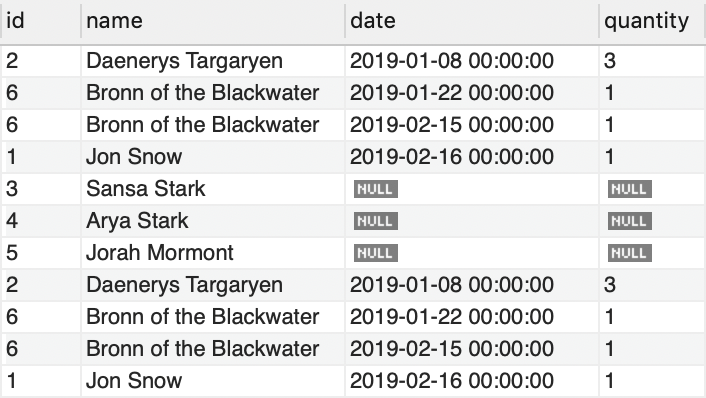
Now, let us join these tables using OUTER JOIN
This query returns customer details, purchase date and quantity
SELECT C.id, C.name, O.date, O.quantity FROM `CUSTOMER` C FULL JOIN `ORDER` O ON C.id = O.customer_id;
NOTE: MySQL does not support outer joins, but you can still achieve the same result by using UNION ALL as shown below:
SELECT C.id, C.name, O.date, O.quantity FROM `CUSTOMER` C LEFT JOIN `ORDER` O ON C.id = O.customer_id UNION ALL SELECT C.id, C.name, O.date, O.quantity FROM `CUSTOMER` C RIGHT JOIN `ORDER` O ON C.id = O.customer_id;
Disclaimer: The example shown above has been tested with MySQL. Depending on your SQL database the CREATE TABLE syntax may vary.