This example demonstrates how to use Servlet’s doPost() method to handle POST requests
In our previous tutorial Java Servlet Example I demonstrated the usage of the doGet() method. Now I am going to show you how to use doPost() method to handle a form POST submission. Java Servlets can handle various types of requests. The list below shows all methods and their purpose
|
METHOD |
SERVLET METHOD |
PURPOSE |
|
GET |
doGet() |
Retrieves the resource at the speci ed URL |
|
HEAD |
doHead() |
Identical to GET, except only the headers are returned |
|
POST |
doPost() |
Typically used for web form submission |
|
PUT |
doPut() |
Stores the supplied entity at the URL |
|
DELETE |
doDelete() |
Deletes the resource identified by the URL |
|
OPTIONS |
doOptions() |
Returns which HTTP methods are allowed |
|
TRACE |
doTrace() |
Used for diagnostic purposes |
Project Structure
In our project we do need three files. pom.xml – to set Maven dependencies and build properties, web.xml – to configure the Servlet and the servlet itself as a java class
Maven pom.xml File
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>net.javatutorial.tutorials</groupId>
<artifactId>ServletPOSTExample</artifactId>
<version>1</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>Servlet POST Example</name>
<url>https://javatutorial.net</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>servletpost</finalName>
<sourceDirectory>src/main/java</sourceDirectory>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.3</version>
<configuration>
<warSourceDirectory>src/main/webapp</warSourceDirectory>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
As in the previous tutorial, we use the dependency javax.servlet-api for our Servlet and the maven-war-plugin to build the web-app
Mapping the Servlet in web.xml File
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd" version="3.1"> <display-name>Simple Servlet Application</display-name> <servlet> <servlet-name>servletPost</servlet-name> <servlet-class>net.javatutorial.tutorials.ServletPOST</servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>servletPost</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/welcome</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
The servlet is given a name “servletPost” which points to the java class ServletPOST
In servlet-mapping we assign the url “/welcome” to our servlet
The Servlet Class
package net.javatutorial.tutorials;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class ServletPOST extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -1641096228274971485L;
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// set response headers
response.setContentType("text/html");
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
// create HTML form
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.append("<!DOCTYPE html>\r\n")
.append("<html>\r\n")
.append(" <head>\r\n")
.append(" <title>Form input</title>\r\n")
.append(" </head>\r\n")
.append(" <body>\r\n")
.append(" <form action=\"welcome\" method=\"POST\">\r\n")
.append(" Enter your name: \r\n")
.append(" <input type=\"text\" name=\"user\" />\r\n")
.append(" <input type=\"submit\" value=\"Submit\" />\r\n")
.append(" </form>\r\n")
.append(" </body>\r\n")
.append("</html>\r\n");
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String user = request.getParameter("user");
response.setContentType("text/html");
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
// create HTML response
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.append("<!DOCTYPE html>\r\n")
.append("<html>\r\n")
.append(" <head>\r\n")
.append(" <title>Welcome message</title>\r\n")
.append(" </head>\r\n")
.append(" <body>\r\n");
if (user != null && !user.trim().isEmpty()) {
writer.append(" Welcome " + user + ".\r\n");
writer.append(" You successfully completed this javatutorial.net example.\r\n");
} else {
writer.append(" You did not entered a name!\r\n");
}
writer.append(" </body>\r\n")
.append("</html>\r\n");
}
}
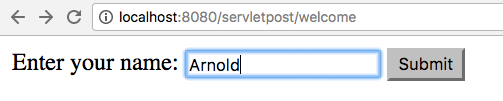
In the code above the doGet() method is used to display the form. The the client (browser) calls the url http://yoururl.com:8080/servletpost/welcome with GET request it sees the form below
The servlet is rendered as HTML in client’s browser, which looks like this:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Form input</title> </head> <body> <form action="welcome" method="POST"> Enter your name: <input type="text" name="user" /> <input type="submit" value="Submit" /> </form> </body> </html>
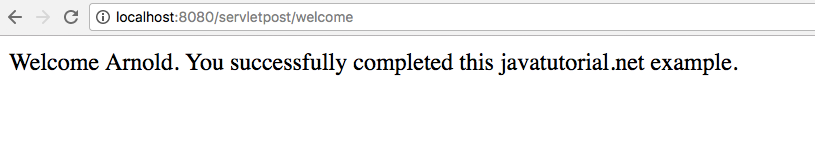
After submit the doPost() method in the servlet is called. Here we build a response based on user’s input. The user receives a greeting message if the name field is filled-out correctly
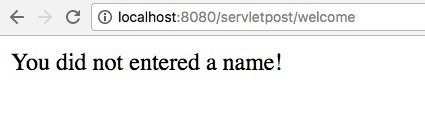
… or a warning message if the name field in the form is left empty
You can find the project source in our GitHub repository.